Use Proxysql for RDS for MySQL or Aurora databases connection pool and Read/Write Split
Serverless connection pooling adapter with proxysql on AWS Fargate and help application better connects to RDS for MySQL or Aurora databases for
- Connection Pooling
- Read/Write Split and Load Balancing
Leverage the reference archiecture project https://github.com/aws-samples/serverless-refarch-for-proxysql.git
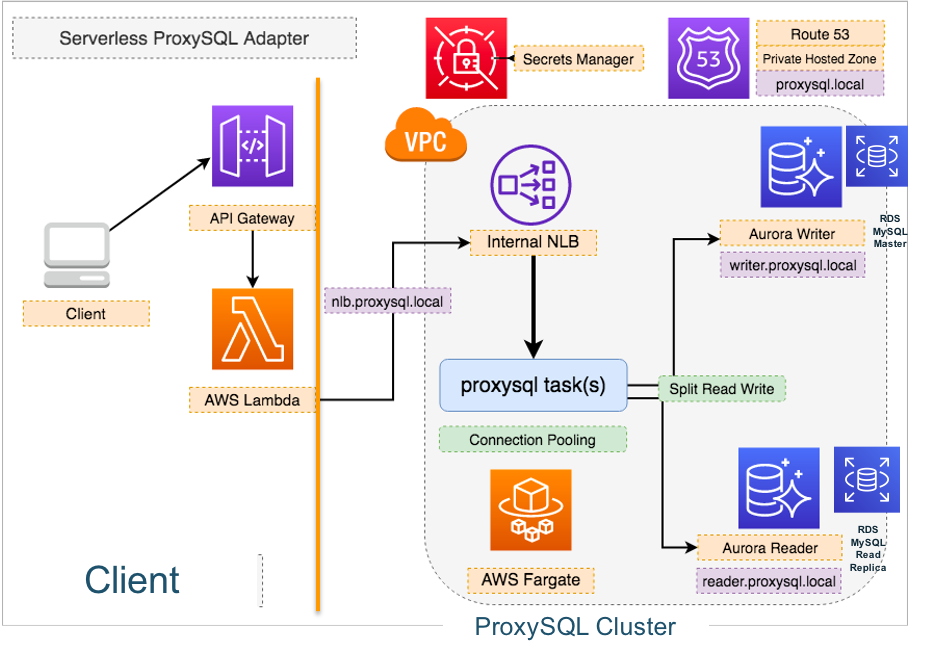
Deploy by CDK
- Clone and install dependency ```bash git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/serverless-refarch-for-proxysql.git
npm install -g aws-cdk cdk –version
cd serverless-refarch-for-proxysql npm install -g aws-cdk npm install
2. Deploy project
```bash
# Check default vpc and existed vpc deployed resource difference
# To check deploying in the default VPC
npx cdk diff -c use_default_vpc=1
# To check deploying in existing VPC
npx cdk diff -c use_vpc_id=vpc-123456
# deploy in vpc-123456
npx cdk deploy -c use_vpc_id=vpc-123456 --profile china-ningxia
# deploy in the default VPC
npx cdk deploy -c use_default_vpc-1 --profile china-ningxia
Notice
- Bootstrap issue ```bash npx cdk deploy -c use_vpc_id=vpc-00d48xxxxxx
Do you wish to deploy these changes (y/n)? y ProxysqlFargateStack: deploying…
❌ ProxysqlFargateStack failed: Error: This stack uses assets, so the toolkit stack must be deployed to the environment (Run “cdk bootstrap aws://account-id/cn-northwest-1”) This stack uses assets, so the toolkit stack must be deployed to the environment (Run “cdk bootstrap aws://account-id/cn-northwest-1”)
Fix:
cdk bootstrap –profile china-ningxia
2. Private subnet
Right now, if I use the existed VPC, I need make sure all private subnets in this VPC must in different AZs. If I my private subnet more than AZ number: e.g 6 subnets cross 3 AZs, it will cause deployment failure.
```bash
A load balancer cannot be attached to multiple subnets in the same Availability Zone
MySQL connect to the ProxySQL admin interface
- How to get the ProxySQL admin interface IP?
Appoarch 1: by ECS Fargate console:
- Clusters -> ProxysqlFargateStack-ProxySQLCluster -> Task
- Get the task private IP
Apporach 2: by CLI
Copy the ProxySQLECSClusterName and ProxySQLECSServiceName from the AWS CDK output, replacing CLUSTER_NAME and ECS_SERVICE_NAME behow
CLUSTER_NAME='ProxysqlFargateStack-ProxySQLCluster942E58CA-T1Yqy82p5Vny'
ECS_SERVICE_NAME='ProxysqlFargateStack-ProxySQLNLBServiceF6E561D2-S3MRJ8BZK2YR'
TASK_ARN=$(aws ecs list-tasks --cluster ${CLUSTER_NAME} --service-name ${ECS_SERVICE_NAME} \
--query 'taskArns[0]' --output text)
TASK_IP=$(aws ecs describe-tasks --cluster ${CLUSTER_NAME} \
--tasks ${TASK_ARN} \
--output text \
--query 'tasks[0].containers[0].networkInterfaces[0].privateIpv4Address')
echo ${TASK_IP}
- Telnet the ProxySQL admin interface 6032 port make sure connection from Same VPC bastion server or peering VPC bastion server
The password can be found in AWS Secrets Manager ProxysqlFargateStack-radmin_pwd secret value
## mysql connect to the proxysql admin interface on Fargate tcp 6032
mysql -uradmin -p -h ${TASK_IP} -P 6032 --prompt 'ADMIN>'
# Let's check the mysql_server_ping_log
ADMIN> SELECT * from monitor.mysql_server_ping_log;
You should see a lot of Access denied errors as proxysql can't connect to the backend because the monitor user does not exists in the backend Aurora.
Connect to the backend Aurora and create a monitor user
Check the DBClusterclusterIdentifier value from the AWS CDK output and replace the value of DB_IDENTIFIER below.
Go to AWS Secrets Manager find the secret ProxysqlFargateStack-auroraMasterSecret value. Replace the DBMasterSecret below.
DB_IDENTIFIER='proxysqlfargatestack-dbclusterdatabased78b6f28-uytcrl1vqsu3'
aws rds modify-db-cluster \
--db-cluster-identifier ${DB_IDENTIFIER} \
--apply-immediately \
--master-user-password <DBMasterSecret>
After 20 seconds, let’s connect the Aurora writer instance with the updated the master password as above
mysql -u admin -p -h writer.proxysql.local --prompt 'WRITER>'
WRITER>CREATE USER monitor@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'monitor';
Now, switch back to the ADMIN> terminal. Make sure the monitor is working
The error message should be NULL now, which indicates the ProxySQL is able to monitor our backend Aurora instances now.
ADMIN>SELECT * from monitor.mysql_server_ping_log;
ADMIN>SELECT * from monitor.mysql_server_connect_log;
(you should see some NULL in the )
Test the mysql read/write through the Proxysql Fargate cluster NLB
- Connect the Aurora by Proxysql Fargate cluster NLB
- Go to AWS Secrets Manager find the secret
ProxysqlFargateStack-auroraMasterSecretvalue as password - Create a demo database and tasks table in it.
mysql -u admin -p -h nlb.proxysql.local --prompt 'ProxysqlNLB>'
ProxysqlNLB> show databases;
ProxysqlNLB> CREATE DATABASE demo;
ProxysqlNLB> USE demo;
ProxysqlNLB> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
task_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP);
ProxysqlNLB> INSERT INTO `tasks` (`title`) VALUES ('foo');
ProxysqlNLB> SELECT * FROM tasks;
- Now get back to the Aurora writer instance
mysql -u admin -p -h writer.proxysql.local --prompt 'WRITER>' WRITER> use demo; WRITER> SELECT * FROM tasks; WRITER> INSERT INTO `tasks` (`title`) VALUES ('bar'); WRITER> SELECT * FROM tasks; - Now get back to the ProxysqlNLB> terminal
mysql -u admin -p -h nlb.proxysql.local --prompt 'ProxysqlNLB>' ProxysqlNLB> SELECT * FROM demo.tasks;The content should be all in sync.
- Connect to the Aurora reader instance
mysql -u admin -p -h reader.proxysql.local --prompt 'READER>' READER> show tables; READER> SELECT * FROM demo.tasks;The content from the reader should be exactly the same with writer and proxy nlb.
Project Code analysis
- serverless-refarch-for-proxysql/dockerAssets.d/proxysql/proxysql.cnf.template
- admin_variables define admin interface
- mysql_variables define mysql connection and monitor configuration info
- mysql_servers define mysql write and read endpoint
- mysql_query_rules define how to do read/write split
- mysql_users define master user
- /serverless-refarch-for-proxysql/dockerAssets.d/proxysql/update.sh
Replace the Placeholder in proxysql.cnf.template with real value and generate the /serverless-refarch-for-proxysql/dockerAssets.d/proxysql/proxysql.cnf
- /serverless-refarch-for-proxysql/dockerAssets.d/proxysql/entrypoint.sh
Start the proxysql
- /serverless-refarch-for-proxysql/dockerAssets.d/proxysql/Dockerfile
The docker file for Fargate container
Connect the proxy from lambda
Follow up the guide Lambda function to access Amazon RDS
- Build the lambda function deployment package ```bash mkdir package && cd package pip install pymysql -t ./ pip install boto3 -t ./ chmod -R 755 . zip -r9 ../function.zip .
cd .. && zip -g function.zip rds_proxysql.py
2. Create lambda function
- SubnetIds: The same subnet groups with Aurora
- SecurityGroupIds: The same security group with Aurora
```bash
db_sg_id=$(aws cloudformation describe-stack-resources --stack-name ProxysqlFargateStack | jq -r '.[][] | select(.ResourceType=="AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup" and (.LogicalResourceId | startswith("DBClusterDatabaseSecurityGroup"))).PhysicalResourceId')
db_subnet_group=$(aws cloudformation describe-stack-resources --stack-name ProxysqlFargateStack | jq -r '.[][] | select(.ResourceType=="AWS::RDS::DBSubnetGroup").PhysicalResourceId')
db_subnet_ids=$(aws rds describe-db-subnet-groups --db-subnet-group-name $db_subnet_group | jq -r '.DBSubnetGroups[].Subnets[].SubnetIdentifier' | awk 'NR > 1 { printf(",") } {printf "%s",$0}')
aws lambda create-function --function-name CreateTableAddRecordsAndRead --runtime python3.7 \
--zip-file fileb://function.zip --handler rds_proxysql.lambda_handler \
--role arn:aws-cn:iam::<account-id>:role/lambda_basic_execution \
--vpc-config SubnetIds=$db_subnet_ids,subnet-061d15db051dbd091,SecurityGroupIds=$db_sg_id
aws lambda invoke --function-name CreateTableAddRecordsAndRead out --log-type Tail \
--query 'LogResult' --output text | base64 -d
# Expected output:
# SUCCESS: Connection to RDS MySQL instance succeeded
# [INFO] 2020-05-28T07:22:15.342Z d89a2cc8-319c-4366-b06a-12e1e9ece843 (1, 'Joe')
# [INFO] 2020-05-28T07:22:15.343Z d89a2cc8-319c-4366-b06a-12e1e9ece843 (2, 'Bob')
# [INFO] 2020-05-28T07:22:15.343Z d89a2cc8-319c-4366-b06a-12e1e9ece843 (3, 'Mary')
aws lambda update-function-code --function-name CreateTableAddRecordsAndRead \
--zip-file fileb://function.zip
Use the existed RDS MySQL
- Create the RDS MySQL master and read replica
```bash
create rds mysql
aws rds create-db-instance –db-name demo –engine MySQL
–db-instance-identifier MySQLForLambdaTest –backup-retention-period 1
–db-instance-class db.t2.micro –allocated-storage 5 –no-publicly-accessible
–master-username admin –master-user-password password
–vpc-security-group-ids $db_sg_id –db-subnet-group-name kops-rds-subnet-group
create rds mysql read-replica
aws rds create-db-instance-read-replica –db-instance-identifier MySQLForLambdaTestRead
–source-db-instance-identifier MySQLForLambdaTest –db-instance-class db.t2.micro
–no-publicly-accessible
–vpc-security-group-ids $db_sg_id
2. Specify the custom MySQL
/serverless-refarch-for-proxysql/bin/index.ts
- writer.mysql.url: `MySQLForLambdaTest` host
- reader.mysql.host: `MySQLForLambdaTestRead` host
```javascript
// new ProxysqlFargate(stack, 'ProxySQL', {
// env,
// vpc: infra.vpc,
// rdscluster
// })
// custom backend
new ProxysqlFargate(stack, 'ProxySQL', {
env,
vpc: infra.vpc,
customBackend: {
writerHost: 'writer.mysql.host',
readerHost: 'reader.mysql.host',
writerPort: '3306',
readerPort: '3306',
masterUsername: 'admin'
}
})
- follow up the guide
MySQL connect to the ProxySQL admin interfaceandConnect to the backend Aurora and create a monitor user``` mysql -u admin -p -h writer.proxysql.local –prompt ‘WRITER>’
WRITER>CREATE USER monitor@’%’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘monitor’;
4. verfy file you can connect to RDS MySQL
```bash
# MySQL Master
mysql -u admin -p -h write.proxysql.local --prompt 'MySQLMaster>'
MySQLMaster> show databases;
MySQLMaster> CREATE DATABASE demo;
MySQLMaster> USE demo;
MySQLMaster> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
task_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP);
MySQLMaster> INSERT INTO `tasks` (`title`) VALUES ('foo');
MySQLMaster> SELECT * FROM tasks;
# MySQL Read replica
mysql -u admin -p -h reader.proxysql.local --prompt 'MySQLReader>'
MySQLReader>use demo;
MySQLReader>show tables;
MySQLReader>SELECT * FROM tasks;
# By ProxyServer NLB
# Note, before https://github.com/aws-samples/serverless-refarch-for-proxysql/issues/14 implemented, you need modify the ProxysqlFargateStack-auroraMasterSecret to existed mysql password and re-create the fargate task
mysql -u admin -p -h nlb.proxysql.local --prompt 'ProxysqlNLB>'
ProxysqlNLB> SELECT * FROM demo.tasks;
ProxysqlNLB> INSERT INTO `tasks` (`title`) VALUES ('bar');
- Verify the lambda code can work
aws lambda invoke --function-name CreateTableAddRecordsAndRead out --log-type Tail \ --query 'LogResult' --output text | base64 -d
cleanup
# lambda
aws lambda delete-function --function-name CreateTableAddRecordsAndRead
# mysql
aws rds delete-db-instance --db-instance-identifier MySQLForLambdaTestRead \
--skip-final-snapshot --delete-automated-backups
aws rds delete-db-instance --db-instance-identifier MySQLForLambdaTest \
--skip-final-snapshot --delete-automated-backups
aws rds wait db-instance-deleted --db-instance-identifier MySQLForLambdaTestRead
aws rds wait db-instance-deleted --db-instance-identifier MySQLForLambdaTest
# cleanup any Route53 record under proxy.local hosted zone
# proxysql
npx cdk destroy