Know How Guide and Hands on Guide for AWS
Port 27017 is the default port for Amazon DocumentDB.
Create an Amazon DocumentDB cluster
Install the mongo shell on EC2 or Cloud 9 environment ```bash
echo -e “[mongodb-org-4.0] \nname=MongoDB Repository\nbaseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/amazon/2013.03/mongodb-org/4.0/x86_64/\ngpgcheck=1 \nenabled=1 \ngpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.0.asc” | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-4.0.repo
sudo yum install -y mongodb-org-shell
wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/rds-downloads/rds-combined-ca-bundle.pem
wget https://s3.cn-north-1.amazonaws.com.cn/rds-downloads/rds-combined-ca-cn-bundle.pem
## Quick start use
1. Connect to your Amazon DocumentDB cluster
Amazon DocumentDB (with MongoDB compatibility) clusters are deployed within an Amazon VPC. They can be accessed directly by Amazon EC2 instances or other AWS services that are deployed in the same Amazon VPC. Additionally, Amazon DocumentDB can be accessed in different VPCs in the same AWS Region or other Regions via `VPC peering`.
- Cross region connection
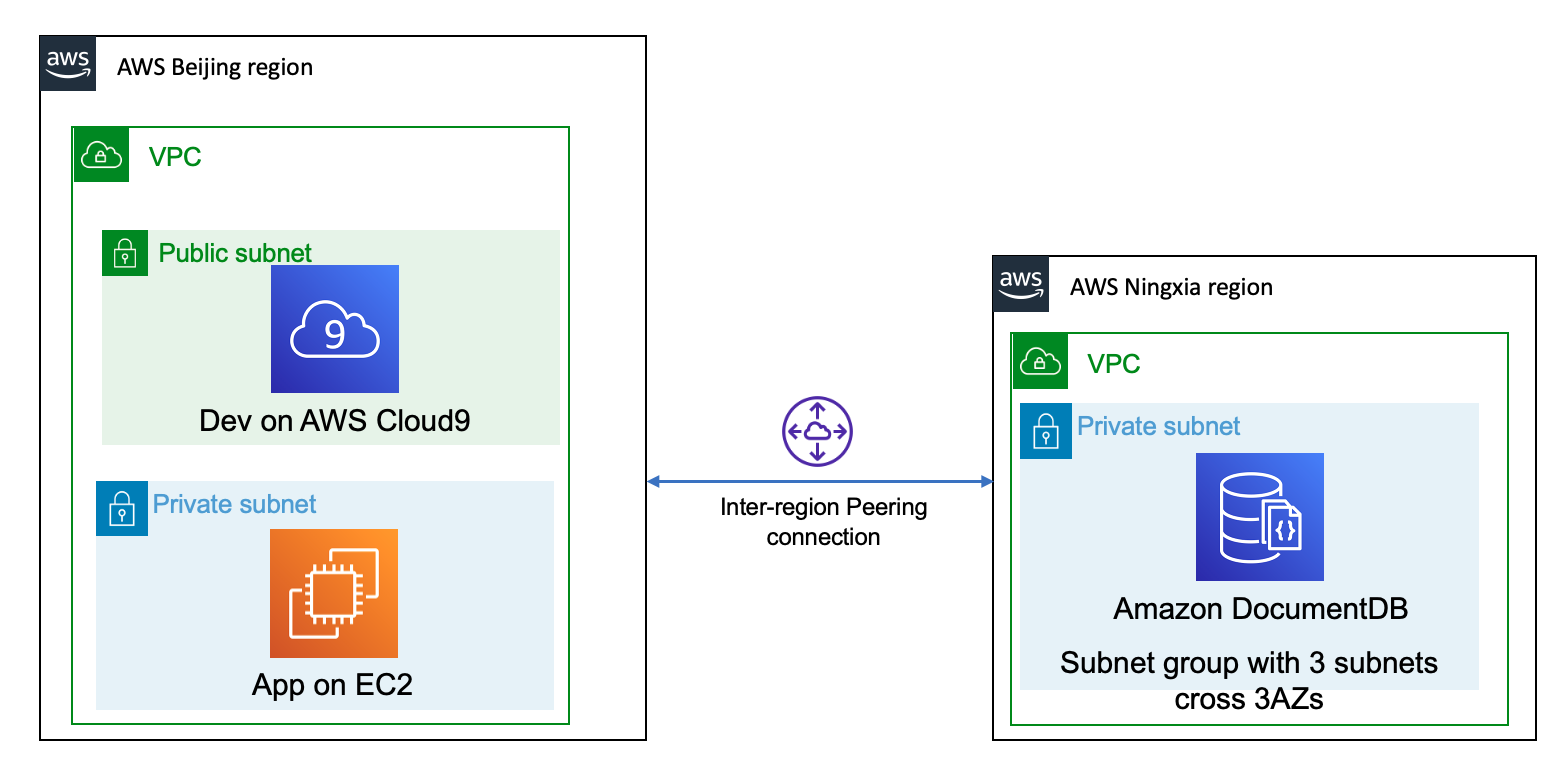
- Inter-region peering

- Application VPC Route Table

- DocumentDB VPC Route Table

If your application) access your Amazon DocumentDB resources from outside the cluster's VPC. In that case, you can use `SSH tunneling` (also known as port forwarding) to access your Amazon DocumentDB resources.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/documentdb/latest/developerguide/connect-from-outside-a-vpc.html
2. Get the conntion info
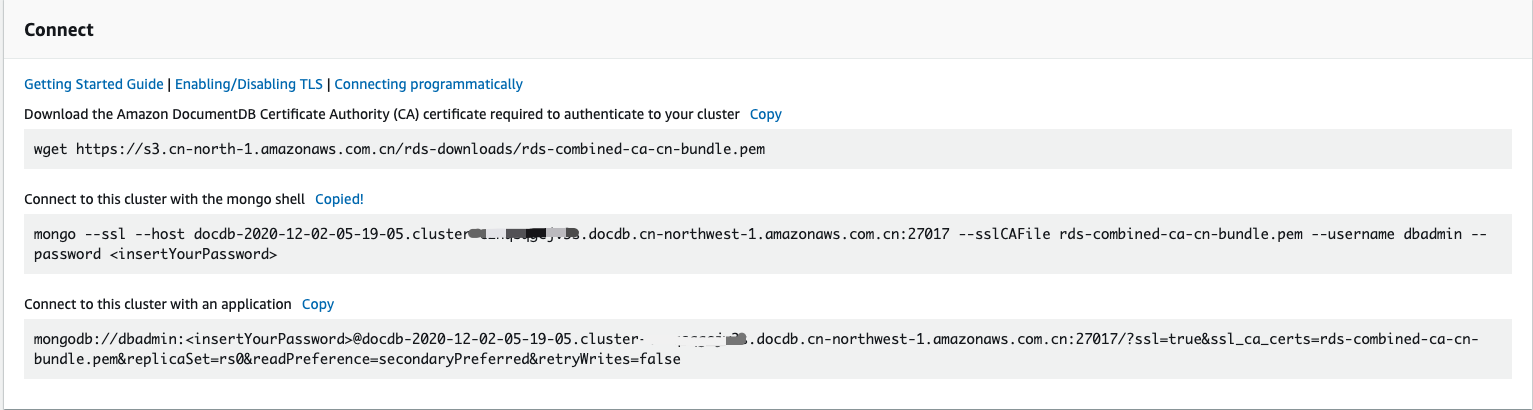
```bash
mongo --ssl --host <docDB_endpoint>:27017 --sslCAFile rds-combined-ca-cn-bundle.pem --username dbadmin --password <insertYourPassword>
When you enter your password and your prompt becomes `rs0:PRIMARY>` prompt, you are successfully connected to your Amazon DocumentDB cluster.
s0:PRIMARY> db.collection.insert({“hello”:”DocumentDB”}) WriteResult({ “nInserted” : 1 })
rs0:PRIMARY> db.collection.findOne() { “_id” : ObjectId(“5fc72948c2e9c52076de75fb”), “hello” : “DocumentDB” }
rs0:PRIMARY> db.profiles.insertMany([ … { “_id” : 1, “name” : “Matt”, “status”: “active”, “level”: 12, “score”:202}, … { “_id” : 2, “name” : “Frank”, “status”: “inactive”, “level”: 2, “score”:9}, … { “_id” : 3, “name” : “Karen”, “status”: “active”, “level”: 7, “score”:87}, … { “_id” : 4, “name” : “Katie”, “status”: “active”, “level”: 3, “score”:27} … ]) { “acknowledged” : true, “insertedIds” : [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ] }
rs0:PRIMARY> db.profiles.find() { “_id” : 1, “name” : “Matt”, “status” : “active”, “level” : 12, “score” : 202 } { “_id” : 2, “name” : “Frank”, “status” : “inactive”, “level” : 2, “score” : 9 } { “_id” : 3, “name” : “Karen”, “status” : “active”, “level” : 7, “score” : 87 } { “_id” : 4, “name” : “Katie”, “status” : “active”, “level” : 3, “score” : 27 }
rs0:PRIMARY> db.profiles.find({name: “Katie”}) { “_id” : 4, “name” : “Katie”, “status” : “active”, “level” : 3, “score” : 27 }
rs0:PRIMARY> db.profiles.findAndModify({ … query: { name: “Matt”, status: “active”}, … update: { $inc: { score: 10 } } … }) { “_id” : 1, “name” : “Matt”, “status” : “active”, “level” : 12, “score” : 202 }
rs0:PRIMARY> db.profiles.find({name: “Matt”}) { “_id” : 1, “name” : “Matt”, “status” : “active”, “level” : 12, “score” : 212 } rs0:PRIMARY>
## Aggregation query
1. Count the Number of Documents in a Collection
```bash
db.sales.insertMany([
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : NumberInt("2"), "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T08:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "jkl", "price" : 20, "quantity" : NumberInt("1"), "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T09:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "xyz", "price" : 5, "quantity" : NumberInt( "10"), "date" : ISODate("2014-03-15T09:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 4, "item" : "xyz", "price" : 5, "quantity" : NumberInt("20") , "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T11:21:39.736Z") },
{ "_id" : 5, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : NumberInt("10") , "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T21:23:13.331Z") },
{ "_id" : 6, "item" : "def", "price" : 7.5, "quantity": NumberInt("5" ) , "date" : ISODate("2015-06-04T05:08:13Z") },
{ "_id" : 7, "item" : "def", "price" : 7.5, "quantity": NumberInt("10") , "date" : ISODate("2015-09-10T08:43:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 8, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : NumberInt("5" ) , "date" : ISODate("2016-02-06T20:20:13Z") },
])
db.sales.aggregate( [ { $group : { _id : "$item" } } ] )
db.sales.aggregate( [
{
$group: {
_id: "$item",
count: { $sum: 1 }
}
}
] )
db.sales.aggregate(
[
// First Stage
{
$group :
{
_id : "$item",
totalSaleAmount: { $sum: { $multiply: [ "$price", "$quantity" ] } }
}
},
// Second Stage
{
$match: { "totalSaleAmount": { $gte: 100 } }
}
]
)
db.sales.aggregate([ // First Stage { $match : { “date”: { $gte: new ISODate(“2014-01-01”), $lt: new ISODate(“2015-01-01”) } } }, // Second Stage { $group : { _id : { $dateToString: { format: “%Y-%m-%d”, date: “$date” } }, totalSaleAmount: { $sum: { $multiply: [ “$price”, “$quantity” ] } }, averageQuantity: { $avg: “$quantity” }, count: { $sum: 1 } } }, // Third Stage { $sort : { totalSaleAmount: -1 } } ])
db.sales.aggregate([ { $group : { _id : null, totalSaleAmount: { $sum: { $multiply: [ “$price”, “$quantity” ] } }, averageQuantity: { $avg: “$quantity” }, count: { $sum: 1 } } } ])
4. Pivot Data
```bash
db.books.insertMany([
{ "_id" : 8751, "title" : "The Banquet", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 8752, "title" : "Divine Comedy", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 1 },
{ "_id" : 8645, "title" : "Eclogues", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 7000, "title" : "The Odyssey", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 },
{ "_id" : 7020, "title" : "Iliad", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 }
])
# Group title by author
db.books.aggregate([
{ $group : { _id : "$author", books: { $push: "$title" } } }
])
# Group Documents by author
db.books.aggregate([
// First Stage
{
$group : { _id : "$author", books: { $push: {"title": "$title", "copies": "$copies"} } }
},
// Second Stage
{
$addFields:
{
totalCopies : { $sum: "$books.copies" }
}
}
])
Amazon DocumentDB Official guide