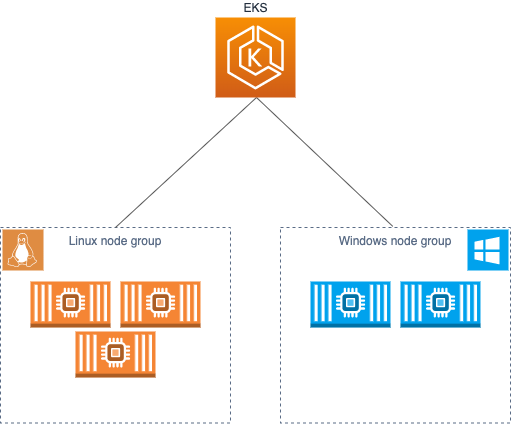
Windows pod in EKS
Overview of Windows support in EKS:
Note: Before deploying Windows nodes, be aware of the considerations such as networking, security and DNS.
EKS workshop for Windows containers
Enabling Windows support
- Check the eksctl version must be 0.24.0 or later. Here assumes that your eksctl version is 0.36.0 or later
eksctl version brew install weaveworks/tap/eksctl - Deploys the VPC resource controller and VPC admission controller webhook that are required on Amazon EKS clusters to run Windows workloads
eksctl utils install-vpc-controllers --cluster eksworkshop --approve --region cn-northwest-1
Launching self-managed Windows nodes.
After you add Windows support to your cluster, you must specify node selectors on your applications so that the pods land on a node with the appropriate operating system. For Linux pods, use the following node selector text in your manifests.
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
kubernetes.io/arch: amd64
For Windows pods, use the following node selector text in your manifests.
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: windows
kubernetes.io/arch: amd64
- Configuring the VPC CNI plugin to use IAM roles for service accounts
```bash
eksctl create iamserviceaccount
–name aws-node
–namespace kube-system
–cluster eksworkshop
–attach-policy-arn arn:aws-cn:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy
–approve
–override-existing-serviceaccounts –region=cn-northwest-1
| kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep aws-node |
#verify that the AWS_WEB_IDENTITY_TOKEN_FILE and AWS_ROLE_ARN environment variables exist kubectl exec -n kube-system ‘aws-node-gtp2r’ env | grep AWS
2. To launch self-managed Windows nodes using eksctl
```bash
eksctl create nodegroup \
--region cn-northwest-1 \
--cluster eksworkshop \
--name eksworkshop-ng-windows-medium \
--node-type t2.medium \
--nodes 1 \
--nodes-min 1 \
--nodes-max 3 \
--node-ami-family WindowsServer2019FullContainer
kubectl get nodes -L kubernetes.io/os \
--sort-by=".status.conditions[?(@.reason == 'KubeletReady' )].lastTransitionTime"
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION OS
ip-192-168-63-228.cn-northwest-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 33h v1.18.9-eks-d1db3c linux
ip-192-168-72-134.cn-northwest-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 33h v1.18.9-eks-d1db3c linux
ip-192-168-49-85.cn-northwest-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 12m v1.18.9-eks-d1db3c windows
- To enable nodes to join your cluster
curl -o aws-auth-cm-windows.yaml https://s3.cn-north-1.amazonaws.com.cn/amazon-eks/cloudformation/2020-10-29/aws-auth-cm-windows.yaml
# Replace the <ARN of instance role (not instance profile) of **Linux** node> and <ARN of instance role (not instance profile) of **Windows** node> snippets with the NodeInstanceRole values that you recorded for your Linux and Windows nodes (you can find in CloudFormation outputs)
kubectl apply -f aws-auth-cm-windows.yaml
kubectl get nodes -L kubernetes.io/os
Deploy a Windows sample application
- Deploy our Windows IIS container ```bash kubectl create namespace windows
kubectl apply -f script/windows_server_iis.yaml
kubectl get pods -n windows -o wide –watch
kubectl -n windows get svc,deploy,pods NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/windows-server-iis-service LoadBalancer 10.100.7.144 xxxxxx.cn-northwest-1.elb.amazonaws.com.cn 80:30843/TCP 26m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/windows-server-iis 1/1 1 1 26m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/windows-server-iis-65f757d98f-m5cq7 1/1 Running 0 26m
2. Testing
```bash
export WINDOWS_IIS_SVC=$(kubectl -n windows get svc -o jsonpath='{.items[].status.loadBalancer.ingress[].hostname}')
curl http://${WINDOWS_IIS_SVC}